Having just received the marks for Module 1: School-based Enquiry (Merit) and Module 3: Developing eLearning (Distinction) of the Masters in Education I am studying towards, I felt that it was time to post an update.
Module 1: School-based Enquiry
A long and thin module that began in September and finished in June, it afforded me the opportunity to conduct a detailed classroom-based investigation. I found writing the essay to be quite difficult. With far too much to say, I felt that the resulting essay was some what disjointed. As such I feel that the garde I achieved was more a reflection of that than the actual research that I conducted. Moreover, on reflection the focus I chose for the module was perhaps too broad.
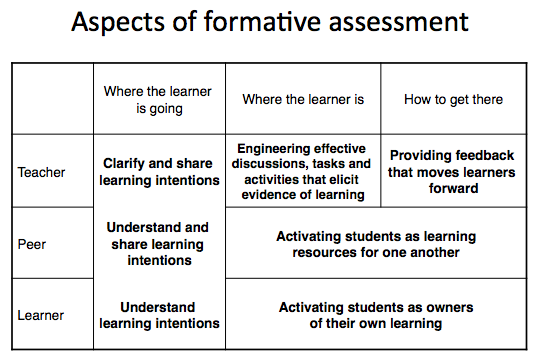
Researching into the impact Google Docs can have on formative assessment was, however, thoroughly enjoyable. It has left me convinced that Google Docs is a perfect tool to develop meaningful AfL practices with students in the Secondary English and Media Studies classrooms. Furthermore, it added validation to a number of conclusions I had already begun to make.
While the grade I achieved does not measure up to the high standards I set in Module 2 or Module 3, this unit taught me more about how to conduct effective classroom-based research and collect data than either of the other two. I believe that this learning process will stand me in good stead as I begin the preparations towards my thesis later in the year.
You can read the assignment here: Does the collaborative functionality of Google Docs allow educators to better put formative assessment at the heart of their students’ learning?
Further information about the module is available here.
Module 3: Developing eLearning
This was (perhaps unsurprisingly) the most enjoyable module of the three I undertook. It certainly played to my strengths, exploring a significant amount of material that I was already well versed in. While this could have negatively impacted on my enjoyment, it actually resulted in providing me with an opportunity to debate and test ideas that I have held for some time.
Like Module 2: Assessment for Learning, this unit ended up being quite personal, giving me the opportunity to evaluate existing practices and to challenge myself to put my money where my mouth is – considering the real benefits of using technology in the classroom. I set my stall out to challenge myself to develop a ReLP that incorporated technologies, enhancing the learning/progress of my students.
The project incorporated iPads + Garageband, Moodle and Google Docs. Writing the essay was far easier, the process of reflection and evaluation in this case was more straightforward. Moreover, learning from the School-based Enquiry, I did a better job of collating and selecting evidence to analyse.
The assignment is available to read here: Design, construct and evaluate a re-usable learning object or process that fulfils a relevant curriculum objective and responds to the learning needs of your pupils. Include a commentary to provide context and explanation of the considerations that you took into account, including relevant points from the literature. References and appendices are here.
More information about the module is available here.
Should you wish to discuss any aspect of the research that I undertook in any of the Modules I have completed, please don’t hesitate to comment below. Alternatively, you can get in touch via email or Twitter.